
Now that you know what the differences are between fume hoods and biosafety cabinets including: how their airflows work, which materials are better suited for each, and the different classes and variations of the two, let’s take a look at a quick rundown of fume hoods and biosafety cabinets:

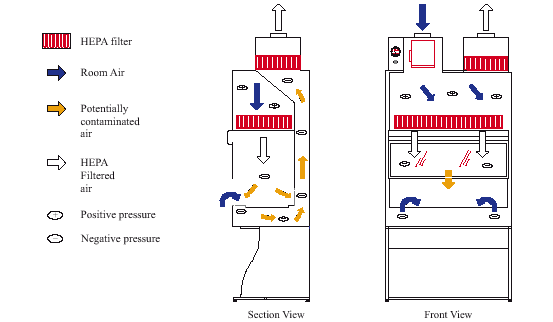
Have an open front, operate under negative pressure and do not provide product protection.Radioactive applications (constructed with additional decontamination features and often require filters in ductwork).Perchloric acid (constructed of acid resistant materials).Some are particularly suited to handle:.Operate on a variable air volume (VAV) system.There are several variations of fume hoods and biosafety cabinets. Here’s a breakdown of their applications and functions: Are gas-tight enclosures, with both intake air and exhaust air passing through HEPA filtrationįume hoods and biosafety cabinets are better suited to handle different types of materials.Intake air is drawn safely around the operator, sterile air flows downward onto the work surface, and exhaust air is HEPA filtered before it is either recirculated into the laboratory or released into the atmosphere either through ductwork or a canopy connection.Air is drawn away from the laboratory worker and across the work surface.Here are the three classes of biosafety cabinets and how they operate: High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters are the main difference between biosafety cabinets and fume hoods, and they will effectively trap all known infectious agents, aerosols, particulates, animal dander, and ensure that only microbe-free exhaust air is discharged from the cabinet. There are three classes of biosafety cabinets and they all have one feature in common: HEPA filtration. Finally, make an effort to keep the sash closed as much as possible. To ensure a safe and productive work environment, do not put your head inside the hood. Refrain from storing large equipment inside the hood or doing anything that could otherwise disrupt the movement of air in any way within the unit. Adequate and continuous airflow is paramount within a fume hood. It is then diluted and released into the atmosphere. Let’s take a look at the specific differences between fume hoods and biosafety cabinets: Airflow Fume Hoodĭue to the hazardous nature of the chemicals that pass through fume hoods, air is drawn away from the lab technician beginning at the face of the equipment, across the work surface and through ductwork. Knowing the level of protection that you require is vital as well, because fume hoods only protect personnel, while biosafety cabinets protect the environment, and the product in addition to protecting personnel. The type of materials you are working with are going to determine which type of laboratory hood you will need.

The main elemental difference between the two is that fume hoods control gases, and biosafety cabinets control particles. Fume hoods and biosafety cabinets look similar and both protect the user, but their functions and applications are different. That’s where fume hoods and biosafety cabinets come into play. A great deal of this research takes place in laboratories.Īs such, those facilities should be well-equipped to protect the health of lab technicians and the integrity of their experiments. In these uncertain times, the importance of scientific research that unearths new, valuable information cannot be overstated.

High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Countertops.Durcon Lab Grade Phenolic Resin Countertops.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
